Calcite (Inventory)/Bell Canopy
From LagWiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
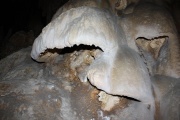
Bell canopies are sheets of flowstone that flare outward as they descend. They terminate before reaching the floor so as to form hood or bell shapes. Bell canopies can form hoods over older formations or be suspended from the ceiling, walls or other speleothems. They form by weathered material that flows as a paste and hardens, or by water that evaporates before dripping off of the edge. | Bell canopies are sheets of flowstone that flare outward as they descend. They terminate before reaching the floor so as to form hood or bell shapes. Bell canopies can form hoods over older formations or be suspended from the ceiling, walls or other speleothems. They form by weathered material that flows as a paste and hardens, or by water that evaporates before dripping off of the edge. | ||
| - | <gallery caption=Gallery perrow= | + | <gallery caption=Gallery perrow=1 widths=300px heights=200px> |
File:Bell canopy.jpg|Bell canopy | File:Bell canopy.jpg|Bell canopy | ||
File:Bell Canopy.jpg|Bell canopy | File:Bell Canopy.jpg|Bell canopy | ||
Revision as of 05:19, 25 July 2013
The Bell Canopy field of the Calcite section should list stations that exhibit a bell canopy.
Bell canopies are sheets of flowstone that flare outward as they descend. They terminate before reaching the floor so as to form hood or bell shapes. Bell canopies can form hoods over older formations or be suspended from the ceiling, walls or other speleothems. They form by weathered material that flows as a paste and hardens, or by water that evaporates before dripping off of the edge.
References
- Palmer, Arthur N. (2007) Cave Geology CAVE BOOKS, Dayton, OH pp 283-284 ISBN-13: 978-0-939748-66-2, ISBN-10: 0-939748-66-5